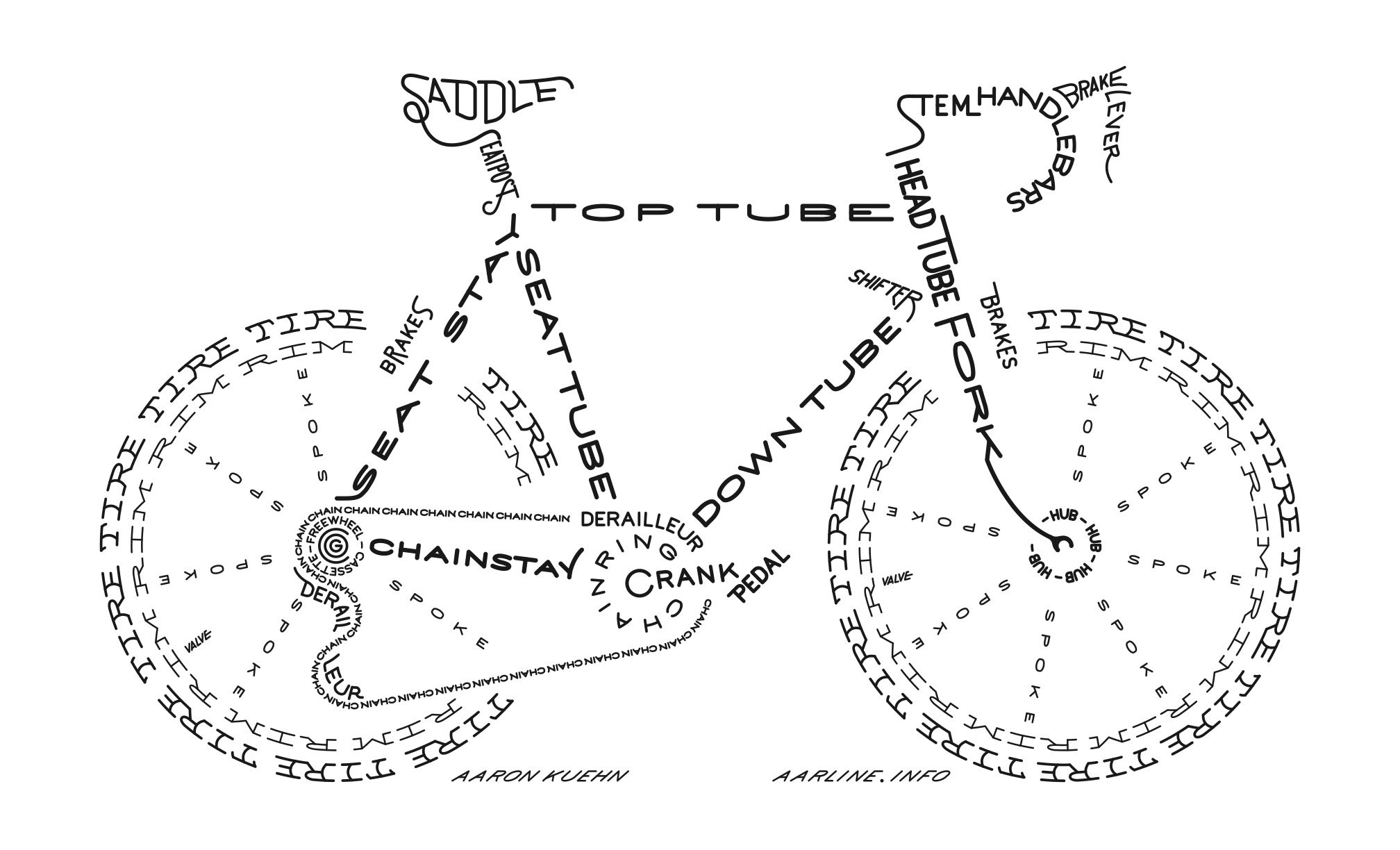
Glossary to help you gain an understanding of Cycling Terms
aerobic: exercise at an intensity that allows the body’s need for oxygen to be continually met. This intensity can be sustained for long periods.
anaerobic: exercise above the intensity at which the body’s need for oxygen can be met. This intensity can be sustained only briefly.
apex: the pointy bit in a turn.
bpm: abbreviation for beats per minute in reference to heart rate.
#bikelash: Negative or hostile reaction to cyclists, especially from motorists or law enforcement. Often perpetuated by 'Shock Jocks' and Talkback radio.
breakaway: a rider or group of riders that has escaped off the front of the pack.
bunch sprint: the dash for the finish line by the main group of riders.
bunch: the main cluster of riders in a race. Also called the group, pack, field or peloton
bunny hop: a way to ride over obstacles such as rocks or logs in which upward body movement lifts both wheels off the ground.
cadence: the number of times per minute that a pedal stroke is completed. Also called pedal rpm.
#carsplaining: when someone who never rides a bike explains road safety to cyclists.
cassette: the set of gear cogs on the rear hub. Also called a freewheel,cluster or block.
chain suck: when the chain sticks to the chainring teeth during a downshift and gets drawn up and jammed between the small ring and the frame.
chainring: a sprocket on the crankset. There may be one, two or three. Short version is ring.
chainstay: the thin frame tube that extends from the rear dropout to the bottom bracket, where the bike's crankset is located. There is a chainstay on each side of the rear wheel.
circuit: a course that is ridden two or more times to compose the race.
cleat: a metal or plastic fitting on the sole of a cycling shoe that engages the pedal.
clincher: a conventional tire with a separate inner tube.
cog: a sprocket on the rear wheel’s cassette or freewheel.
criterium: a mass-start race covering numerous laps of a course that is normally about one mile or less in length.
cycling specific clothing: refers to clothing used only for cycling, this can refer to shoes with cleats, lycra or sports wear and other items used to ride that would not be worn when not riding. (Cafes don't count) :) .
downshift: to shift to a lower gear, i.e. a larger rear cog or smaller front chainring.
drafting: riding closely behind another rider to take advantage of the windbreak (slipstream) which uses about 30 percent less energy. Also called sitting in or wheel-sucking.
drive train: the components directly involved with making the rear wheel turn, i.e. the chain, crankset and cassette. Also called the power train.
dropout: frond on the frame, the slots into which the front and rear wheel axles fit.
drop off the back: describes one or more riders who have failed to keep pace with the main group.
drops: the lower part of a down-turned handlebar typically found on a road bike. The curved portions are called the hooks.
electrolytes: fluid substances such as sodium, potassium, and chloride that are necessary for maintaining hydration levels.
ergo: a stationary, bicycle-like fan resistance front wheel for indoor training.
fixed gear: a direct-drive bike using one chain ring on the front and one rear cog on the back of a bike. When the rear wheel turns so do the chain and cranks - coasting isn't possible.
glycogen: a fuel derived as glucose (sugar) from carbohydrate stored in the muscles and liver. It’s the primary energy source for high-intensity cycling. Reserves are normally depleted after about two-and-a-half hours of riding.
granny gear: the lowest gear ratio, combining the small chainring with the largest cassette cog. It’s mainly used for very steep climbs.
hammer: to ride strongly in big gears.
headset: the parts at the top and bottom of the frame's head tube, into which the handlebar stem and fork are fitted.
hybrid: a bike that combines features of road and mountain bikes. Also called a cross bike, city bike or hybrid bike.
jump: a quick, hard acceleration.
lactate threshold (LT): the exertion level beyond which the body can no longer produce energy aerobically, resulting in the build up of lactic acid. This is marked by muscle fatigue, pain and shallow, rapid breathing. Also called anaerobic threshold (AT).
lactic acid: a substance formed during anaerobic metabolism when there is incomplete breakdown of glucose. It rapidly produces muscle fatigue and pain. Also called lactate.
normal riding: normal riding refers to the attire one wears when riding and not to the style of riding. If a person has to get changed or put on 'cycling specific' clothing, then they are not 'normal riding'. Normal riding is commonly refered to as dutch riding, this is because most people in the Netherlands do not use 'cycling specific' clothing to ride there bikes.
panniers: large bike bags used by touring cyclists or commuters. Panniers attach to racks that place them low on each side of the rear wheel, and sometimes the front wheel.
peak body: an organisation which represents an entire sector of industry or the community to the government, often incorporating other organisations in that area.
peloton: the main group of riders in a race or large event (pronounced pel-a-ton)
pinch flat: an internal puncture marked by two small holes caused by the tube being squeezed against the rim. It results from riding into an object too hard for the air pressure in the tube. Also called a snakebite.
presta: the narrow European-style valve found on some inner tubes. A small metal cap on its end must be unscrewed before air can enter or exit.
psi: abbreviation for pounds per square inch. The unit of measure for tire inflation and air pressure in some suspensions.
pull off: to move to the side after riding in the lead so that another rider can come to the front.
pull, pull through: take a turn at the front.
road race: a mass-start race on pavement that goes from point to point, covers one large loop or is held on a circuit longer than those used for criteriums.
rollers: an indoor training device consisting of three long cylinders connected by belts. Both bike wheels roll on these cylinders so that balancing is much like actual riding.
saddle sores: skin problems in the groin that develop from chafing caused by pedaling action. Sores can range from tender raw spots to boil-like lesions if infection occurs.
sag wagon: a motor vehicle that follows a group of riders, carrying equipment and lending assistance in the event of difficulty.
schraeder: an inner tube valve identical to those found on car tires. A tiny plunger in the centre of its opening must be depressed for air to enter or exit.
seat stay: the thin frame tube that extends from the rear dropout to the top of the seat tube. There is a seat stay on each side of the rear wheel.
single track: a trail so narrow that two cyclists can’t easily ride side by side, which makes passing difficult or impossible.
sit on a wheel: to ride in someone's draft.
slipstream: the pocket of calmer air behind a moving rider. Also called the draft.
soft-pedal: to rotate the pedals without actually applying power.
stage race: a multi-day event consisting of various types of races. The winner is the rider with the lowest elapsed time for all races (stages).
turn: the time spent by a cyclist leading the bunch into the wind
upshift: to shift to a higher gear, ie. a smaller cog or larger chain ring.
velodrome: an oval banked track for bicycle racing.
watt: a measurement of power produced which tells how much force is applied to the pedals. A power output of 100 watts will illuminate a 100-watt light bulb.
And to make it easy to see where everything goes: